Why is on-page SEO so important?
Of course your classic on-page SEO tweaks still work. Even better than before actually. And I’m not the only one who says that. Take it from
Google too.
Behind those fancy AI-based algorithm updates lie your usual keyword optimization hacks. With no keyword input and relevant related words, Google’s bots simply wouldn’t be able to understand your content and place it where relevant.
Other studies like this one from Backlinko also justify the use of on-page SEO methods. Just run any search for a competitive keyword and you’ll notice most websites try to keep their on-page factors clean and relevant.
When done the right way, optimizing your pages for optimal ranking can also:
- Boost, even double, your website traffic
- Bring in more leads
- Improve your click-through-rates
- Increase time on page
- Reduce bounce rates
- Match reader intent
- Position you as a thought leader in your industry
- And so much more!
- On-page SEO factors to optimize right away
But you have so many factors to optimize, where do you start?
Below are all the on-page SEO factors that are worth your time:
1. SEO-friendly URL
Short URL that includes the keyword.
As an example:
www.domain.com/blog/on-page-seo
is better than a default URL
www.domain.com/blog/sfeogytytuyjyj.html
or a long one
www.domain.com/blog/on-page-seo-factor-to-optimize-this-year.html
or the other likes.
Make sure you think this through before you publish the article. Changing the URL after will make you lose your links unless you add a redirect.
Another issue to pay attention to is to make sure you won’t be using the same keyword in another URL for a more profitable page.
For instance, if you’re an SEO agency you might want a page like:
www.domain.com/on-page-seo
But if you later decide to also put together a guide for the same keyword, you won’t be able to use the same URL so you’ll have to publish it on your blog as www.domain.com/blog/on-page-seo or change the URL.
2. Title Tag
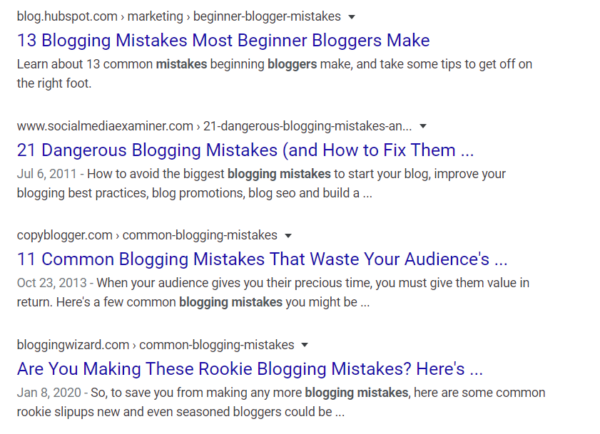
Your main keyword should ideally be placed at the beginning of your title. Especially in the case of the SEO title. You can set this one separately from the Yoast WordPress plug-in.
Here are 4 examples for the “blogging mistakes” keyword where the 1st result is optimal:
The SEO title is not final like the URL so you can change it at any time after publishing the post.
If you’ve got a bit more time, do some A/B testing on your SEO title. Change it every 3-4 months to see which one works best for your CTR.
3. Headings! Headings!
Nailing the keyword optimization of your headings is so important, yet so many writers seem to skip this part.
You’ve got multiple options here:
Take your main keyword and create natural headings around it. This means your keyword will appear in 2-3 headings.
Place your main keyword in the 2-3 headings mentioned at point 1 and optimize the rest of your headings for secondary keywords.
Above all, remember to include at least H2s and H3s in your text. [like this article, btw] Ideally, you’d have separate designs for these so they are easily distinguishable by readers.
4. The first 100 words
Another ignored on-page SEO factor is including your keyword in the first 100 words of your article. I don’t always do this because sometimes it doesn’t seem natural to shove a keyword in the first few words since you might want to set the scene first.
But if you can manage to add it in the first sentence, way to go! Google will automatically consider this topic is of top importance to the article and thus crawl it accordingly.
5. Frequent keywords, but no stuffing!
Stuffing is actually quite hard to do these days without readers reporting your content.
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Webcast, March 5th: How AI Can Find Opportunities and Shorten Your Sales Cycles
REGISTER NOW
Keyword stuffing looks something like:
These are our blog blogging blogger tips for bloggers who blog on blogs for bloggers…
Not cool. I know.
Instead, natural keyword frequency looks more like:
We’ve put together this list of tips for first-time bloggers who are looking to improve the quality of their blog posts…
And then just use your keywords sparingly and in a natural way throughout the entire article.
6. Outbound links
These are the links you add to relevant content on other websites. The general rule (or best practice if you want to) is to only link to materials that will be of value to your readers or support your claims.
You can try my trick and create a strategy to always follow for this. For instance, I only link to reports or studies and occasionally to external tools readers might want to test.
Don’t add too many though. Google didn’t disclose a number of outbound links that’s ok to use, but most blog guidelines [and my own experience] will accept a maximum of 3 links.
Also, try not to link to content that targets the same keyword you want to aim for. Google will automatically think that even you consider that content is better so it will be much more difficult to rank higher than that competitor.
7. Internal links
We’ve got two situations here.
The first case is when you add links to your other blog posts or web pages in this article you’re currently putting together. By all possible means, make sure the links are relevant to your topic.
The second instance happens after you publish your article. Try to find 2-3-4 of your other posts that are relevant to your new post and place a link to this new article on relevant keywords only.
Disclaimer: Avoid link stuffing. This means you shouldn’t use your top-performing article to link to every possible post of yours.
For all external and internal links, make sure you check them regularly so the links are not broken or the content there hasn’t fundamentally changed and no longer matches your needs.
8. Page speed
Smaller images, enable file compression, reduce redirects, minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML, improve your server’s response time, and anything else PageSpeedInsights tells you to change.
9. Responsive design
Google has been seriously penalizing websites that are not responsive.
Mobile traffic is still growing so even if you don’t believe Google will have a say, your readers will when they won’t be able to click your call-to-action button.
10. Meta description
This is the small snippet of content that users will see under your SEO title in the search results.
Two secrets here:
Include your keyword for Google.
Include a CTA or an enticing fact or incentive to make people want to click on your post. This will also boost your click-through-rate.
Yes, the meta description too can be changed even years after first publishing the article.
Go way back in your blog’s history and check all meta descriptions. You’ll be surprised to discover missing ones too.
11. Review the readers’ intent
So you have this post that ranked well for 2 years but then it died. Do a SERP research again to see if the readers’ intent has changed or maybe your competitors managed to answer better to their needs.
This is also a perfect time for you to review the entire structure of the article and run a new keyword research to check for new potential secondary keywords to target. Keyword volumes and difficulty can change often. Every week even. So keeping an eye on the evolution of the keywords that are highly valuable for your business is vital to ensure you maintain your position.
12. Remove duplicate content in all its forms
Canonical links will be your best friend here. Especially for e-commerce websites who commonly have duplicate content on their category pages.
But even if you’re not an e-commerce website, I recommend making sure you have the canonical link set for every page of yours. Yes, that includes articles.
A much-too-common issue beginner marketers make is adding their blog posts to multiple categories or tags on their blog. This inevitably creates duplicate content so bear through the temptation and stick to one category.
13. ALT tags and file names
You’re probably already aware that the keyword your want to rank for should also be part of your ALT text in at least one image. [Still, try to add ALT tags to all images and include secondary keywords in them.]
Disclaimer: Don’t do keyword stuffing here either. A good ALT tag is “blogging mistakes for beginners”. A bad ALT tag looks like this “blogging mistakes bloggers blogs beginner mistakes”
What many writers are still not aware of is the importance of having keywords in the file name of your images as well. You know, blogging-mistakes.png instead of screenshot56.png.
14. Data markup
This only applies to specific websites where you want to post news, reviews, recipes, and the likes.
Your results will appear like:
Instead of:
So many options here that can be added and tested at all times. Heach to Schema.org for all the details to see if there’s anything right for your blog type.
15. Got social media?
If you don’t yet have social media sharing buttons on your posts, go right now and get a plug-in. Many tools let you customize the text readers will share (or at least the suggestion) so they can bring in more views via their own networks.
16. No more black hat techniques!
Finally, make sure your website is free of any black hat SEO techniques. These include spammy links, cloaking, doorway pages, hidden text and links, spam comments, duplicate content, link farms, paid links even.
Surprisingly or not, Google is starting to pick up on paid links. That’s why many large websites strictly prohibit selling links on their website. Unfortunately, you’ll still occasionally receive emails from writers who are willing to provide such links. Just say no. It’s cheaper, more valuable, and easier to become an author on that website yourself anyway.
Where to take your on-page SEO efforts next?
Bookmark this article or create your own checklist of everything you need to change. If possible, make sure you analyze all of these on-page SEO factors and how they perform on your own pages.
I won’t lie to you and tell you the process is easy or quick. It can take months if you have a year’s worth of content or more.
But it’s worth it!
Got any extra tips on optimizing the on-page SEO factors for your website? What has worked for you and where are you still experimenting? Let us know!
Read more at: business2community.com